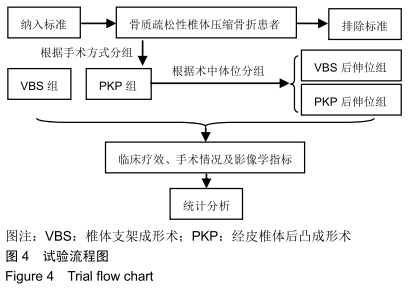
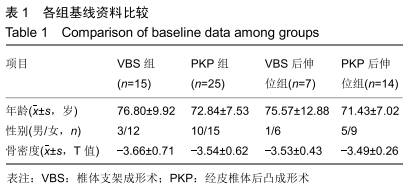
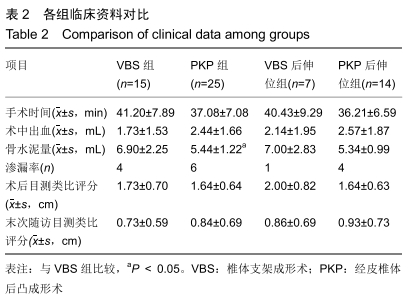
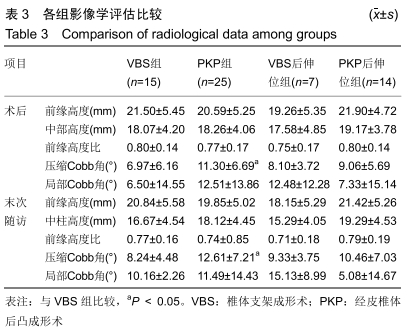
[1] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J].中国全科医学,2017,20(32):3963-3982.
[2] ALEXANDRU D, SO W. Evaluation and management of vertebral compression fractures. Perm J. 2012;16(4):46-51.
[3] EVANS AJ, JENSEN ME, KIP KE, et al. Vertebral compression fractures: pain reduction and improvement in functional mobility after percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty retrospective report of 245 cases. Radiology. 2003;226(2):366-372.
[4] MCGIRT MJ, PARKER SL, WOLINSKY JP, et al. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: an evidenced-based review of the literature. Spine J. 2009;9(6):501-508.
[5] LEDLIE JT, RENFRO M. Balloon kyphoplasty: one-year outcomes in vertebral body height restoration, chronic pain, and activity levels. J Neurosurg. 2003;98(1 Suppl):36-42.
[6] WEBER CH, KROTZ M, HOFFMANN RT, et al. CT-guided vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: comparing technical success rate and complications in 101 cases. Rofo. 2006;178(6): 610-617.
[7] VOGGENREITER G. Balloon kyphoplasty is effective in deformity correction of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine.2005;30(24):2806-2812.
[8] HEINI PF, TEUSCHER R. Vertebral body stenting/ stentoplasty. Swiss Med Wkly. 2012;142:w13658.
[9] VANNI D, GALZIO R, KAZAKOVA A, et al. Third-generation percutaneous vertebral augmentation systems. J Spine Surg. 2016;2(1):13-20.
[10] KLEZL Z, MAJEED H, BOMMIREDDY R, et al. Early results after vertebral body stenting for fractures of the anterior column of the thoracolumbar spine. Injury. 2011;42(10): 1038-1042.
[11] ROTTER R, MARTIN H, FUERDERER S, et al. Vertebral body stenting: a new method for vertebral augmentation versus kyphoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(6):916-923.
[12] 杜桂迎,余卫,林强,等.WHO双能X线吸收仪骨质疏松症诊断标准及其相关问题[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016,9(3): 330-338.
[13] JOYCE CR, ZUTSHI DW, HRUBES V, et al. Comparison of fixed interval and visual analogue scales for rating chronic pain. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1975;8(6):415-420.
[14] 周毅,海涌,苏庆军,等.影响椎体后凸成形术椎体高度恢复的相关因素及临床意义[J].中国骨与关节外科,2011,4(4):288-93.
[15] KUKLO TR, POLLY DW, OWENS BD, et al. Measurement of thoracic and lumbar fracture kyphosis: evaluation of intraobserver, interobserver, and technique variability. Spine. 2001;26(1):61-65; discussion 66.
[16] PHILLIPS FM, HO E, CAMPBELL-HUPP M, et al. Early radiographic and clinical results of balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine. 2003;28(19):2260-2265; discussion 5-7.
[17] CUI L, CHEN L, XIA W, et al. Vertebral fracture in postmenopausal Chinese women: a population-based study. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(9):2583-2590.
[18] LEE HM, PARK SY, LEE SH, et al. Comparative analysis of clinical outcomes in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs): conservative treatment versus balloon kyphoplasty. Spine J. 2012;12(11):998-1005.
[19] 陈小兵,赵洪普.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折不同时期保守和微创治疗的疗效比较[J].中国全科医学,2015,18(35):4320-4324.
[20] 印平,马远征,马迅,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的治疗指南[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):643-648.
[21] 杨富国,杨波,尹飚,等.椎体成形结合抗骨质疏松治疗减少再骨折发生率[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(33):4905-4912.
[22] 赵国权,杨圣,罗春山.PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(1):106-109.
[23] SCHMIDT R, CAKIR B, MATTES T, et al. Cement leakage during vertebroplasty: an underestimated problem? Eur Spine J. 2005;14(5):466-473.
[24] YOO KY, JEONG SW, YOON W, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with pulmonary cement embolism following percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate. Spine. 2004;29(14):E294-E297.
[25] CHEN HL, WONG CS, HO ST, et al. A lethal pulmonary embolism during percutaneous vertebroplasty. Anesth Analg. 2002;95(4):1060-1062.
[26] GRADOS F, DEPRIESTER C, CAYROLLE G, et al. Long-term observations of vertebral osteoporotic fractures treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty. Rheumatology(Oxford). 2000; 39(12):1410-1414.
[27] FÜRDERER S, ANDERS M, SCHWINDLING B, et al. Vertebral body stenting. A method for repositioning and augmenting vertebral compression fractures. Orthopade. 2002;31(4):356-361.
[28] MUTO M, GRECO B, SETOLA F, et al. Vertebral body stenting system for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: follow-up at 12 months in 20 cases. Neuroradiol J. 2011;24(4):610-619.
[29] MARTIN-LOPEZ JE, PAVON-GOMEZ MJ, ROMERO-TABARES A, et al. Stentoplasty effectiveness and safety for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a systematic review. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(5): 627-632.
[30] WERNER CM, OSTERHOFF G, SCHLICKEISER J, et al. Vertebral body stenting versus kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(7):577-584.
[31] CAPEL C, FICHTEN A, NICOT B, et al. Should we fear cement leakage during kyphoplasty in percutaneous traumatic spine surgery? A single experience with 76 consecutive cases. Neurochirurgie. 2014;60(6):293-298.
[32] 马俊.经皮椎体后凸成形术与经皮椎体成形治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折的疗效比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(6): 571-573.
[33] SCHÜTZENBERGER S, SCHWARZ SM, GREINER L, et al. Is vertebral body stenting in combination with CaP cement superior to kyphoplasty? Eur Spine J. 2018;27(10): 2602-2608.
|